The Great Read
Jordan Belfort, the inspiration for “The Wolf of Wall Street,” is marketing himself as a cryptocurrency guru.
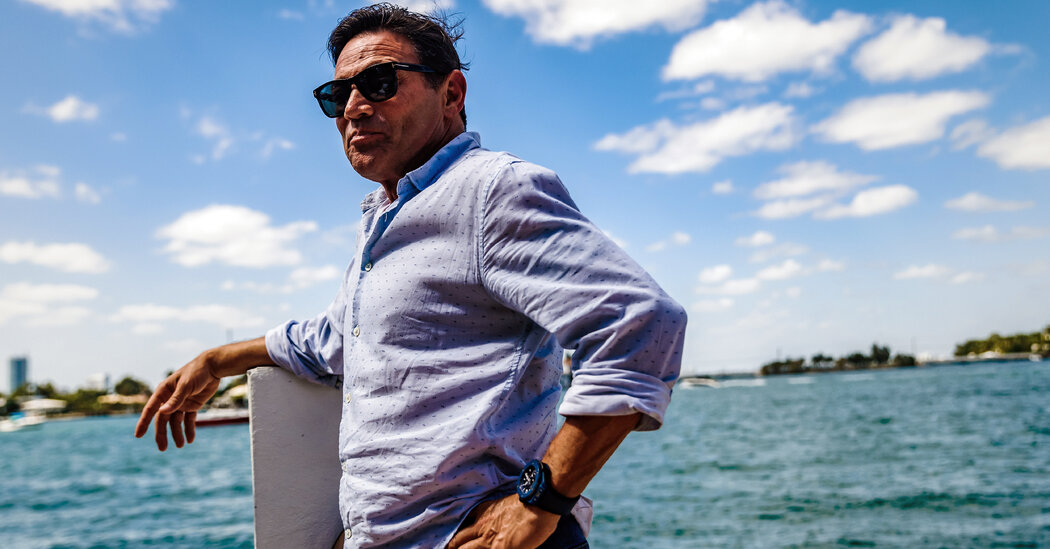
Until recently, Jordan Belfort was a crypto skeptic. Now he charges entrepreneurs tens of thousands for his advice on it. Credit…Scott McIntyre for The New York Times
Supported by
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
To hear more audio stories from publications like The New York Times, download Audm for iPhone or Android.
MIAMI BEACH — Jordan Belfort was lounging by the pool on a sunny April morning, sipping Red Bull and sharing a cautionary tale. Not the usual one about his imprisonment on 10 counts of securities fraud and money laundering: This time, he’d been the victim. Last fall, he explained to a group of businessmen gathered at his palatial home, a hacker had stolen $300,000 of digital tokens from his cryptocurrency wallet.
He had gotten the bad news at dinner on a Friday, he said, while he was telling a venture-capitalist friend about the time he sank his yacht during a drug-fueled romp in the mid-90s. After breaking into Mr. Belfort’s account, the hacker transferred large quantities of Ohm, a popular cryptocurrency token, to a separate wallet — a publicly visible transaction Mr. Belfort could do nothing to reverse. “You can see where the money is,” he said. “It’s the most frustrating thing.”
Mr. Belfort, 59, is best known for “The Wolf of Wall Street,” a tell-all memoir about his debauched 1990s career in high finance, which the director Martin Scorsese adapted into a 2013 movie starring Leonardo DiCaprio as the hard-partying protagonist. These days, the real-life Mr. Belfort is a consultant and sales coach, charging tens of thousands of dollars for private sessions.
This month, at his house in Miami Beach, he hosted nine blockchain enthusiasts and entrepreneurs for a weekend-long crypto workshop — a chance to hang out with the Wolf and enjoy an “intimate financial experience” with his crypto-industry friends.
A long line of celebrities has tried to profit from the cryptocurrency boom, appearing in widely mocked crypto commercials or flogging nonfungible tokens, the unique digital collectibles known as NFTs. Mr. Belfort said he had refused to participate in the worst of the shilling. He has declined offers to launch a line of Wolf-themed NFTs, he said, even though “I could easily make $10 million.”
He is also a recent convert away from crypto skepticism. Not long ago, he shot a YouTube video about the dangers of Bitcoin, which he called “frickin’ insanity” and “mass delusion.” Over the years, he said, he gradually changed his mind, as he learned more about cryptocurrencies and prices skyrocketed.
Now, Mr. Belfort is an investor in a handful of start-ups, including a new NFT platform and an animal-themed crypto project that he said was “trying to take the dog-and-pet ecosystem and put it onto the blockchain.”
Whatever his crypto bona fides, Mr. Belfort is unquestionably qualified to discuss the subject of financial fraud, a major problem in the digital-asset industry. In the 1990s, the firm he founded, Stratton Oakmont, operated a sophisticated stock-manipulation scheme. At the height of their wealth, he and his business partners consumed enormous quantities of cocaine and quaaludes and regularly employed prostitutes. Mr. Belfort eventually served 22 months in prison.
Given that history, it can feel slightly surreal to hear an older, more grizzled Mr. Belfort proclaim that he is “massively looking forward to regulation” in the crypto industry. “I’m not interested in separating people from their money,” he said. “That’s the opposite of how I act right now.”
Still, the crypto workshop at his house was not free: Guests paid one Bitcoin for a seat, or the cash equivalent, which is roughly $40,000.
The workshop began at 9 a.m. on Saturday. The guests — chosen from a pool of more than 600 applicants — milled around Mr. Belfort’s backyard, eating made-to-order omelets and trading tips about Bitcoin mining and tokenomics. A crypto miner from Kazakhstan relaxed in the sun with an aspiring blockchain influencer who runs a roofing company in Idaho. A Florida businessman explained his plan to use NFTs in a start-up that he’s pitching as Tinder for music. Some of the guests said they had paid for the workshop because they were die-hard fans of the Wolf; others simply wanted to network with fellow entrepreneurs.
By 9:15 a.m., the mimosas were flowing, but Mr. Belfort was nowhere to be seen. “The U.S. dollar is going to crap,” said the roofing executive, Doug Bartlett. A few minutes passed. Still no Wolf. “The Wolf is still sleeping?” one guest wondered aloud.
At last, Mr. Belfort emerged from the house, wearing faded jeans and dark sunglasses. Mr. Belfort has short dark hair; he’s more wrinkled than he was in the ’90s, but his face is still set in a perpetually boyish grin. He stopped on the staircase down from the porch to survey the scene: nine men dressed in various shades of business casual — polo shirts, flip-flops, untucked button-down shirts.
“I guess we still need to work on feminine adoption of cryptocurrency,” he said. “We got to get some girls here next year.” He paused. “Women.”
Someone handed Mr. Belfort a can of Red Bull. (It was about 9:30 a.m.) “I’m gonna need the sugar,” he said. After a few minutes of chitchat, he ushered the group into the dining room, where each place at the table was set with a notebook and a copy of “Way of the Wolf,” a sales manual Mr. Belfort published in 2017.
Mr. Belfort has spent the past two decades trying to rebuild his reputation, but signs of the old Wolf were everywhere. Behind his spot at the head of the table, a fully stocked liquor shelf took up most of the wall. (He hasn’t gotten high in 25 years, he said, but he sometimes drinks.) Next to the shelf hung a poster designed to resemble an entry on the periodic table — Qu for quaalude — listing various “drug facts,” including “best sex ever.”
After a round of introductions, Mr. Belfort began a lecture on the minutiae of cryptocurrencies, from the differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum to the rise of decentralized autonomous organizations. He shared his wisdom on crypto-based “smart contract” systems (“some of them are really smart; some of them are stupid”) and recounted old stories about his collaboration with Leo and Marty.
“Leo had never done drugs,” he said. “I had to educate him on that.”
For a gathering of crypto evangelists, it was striking how much time everyone spent reliving his biggest losses. Nearly half the group said they’d been hacked. One guest said he’d lost money when the cryptocurrency exchange Mt. Gox collapsed in 2014. Two others said they’d burned large quantities of tokens in risky trades.
The energy in the room lifted with the arrival of Chase Hero, one of a series of guest speakers Mr. Belfort had recruited for the weekend. A crypto investor and gaming enthusiast, Mr. Hero declared that stablecoins — cryptocurrencies whose value is pegged to the U.S. dollar — were “the biggest innovation since sliced bread.”
“It seems vivacious and insane and almost borderline a Ponzi scheme,” Mr. Hero said of his favorite stablecoin project. “Which makes it the perfect asset for cryptocurrency because that’s what these kids love.”
A glossary. Cryptocurrencies have gone from a curiosity to a viable investment, making them almost impossible to ignore. If you are struggling with the terminology, let us help:
Bitcoin. A Bitcoin is a digital token that can be sent electronically from one user to another, anywhere in the world. Bitcoin is also the name of the payment network on which this form of digital currency is stored and moved.
Blockchain. A blockchain is a database maintained communally and that reliably stores digital information. The original blockchain was the database on which all Bitcoin transactions were stored, but non-currency-based companies and governments are also trying to use blockchain technology to store their data.
Cryptocurrencies. Since Bitcoin was first conceived in 2008, thousands of other virtual currencies, known as cryptocurrencies, have been developed. Among them are Ether, Dogecoin and Tether.
Coinbase. The first major cryptocurrency company to list its shares on a U.S. stock exchange, Coinbase is a platform that allows people and companies to buy and sell various digital currencies, including Bitcoin, for a transaction fee.
DeFi. The development of cryptocurrencies spawned a parallel universe of alternative financial services, known as Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, allowing crypto businesses to move into traditional banking territory, including lending and borrowing.
NFTs. A “nonfungible token,” or NFT, is an asset verified using blockchain technology, in which a network of computers records transactions and gives buyers proof of authenticity and ownership. NFTs make digital artworks unique, and therefore sellable.
Web3. The name “web3” is what some technologists call the idea of a new kind of internet service that is built using blockchain-based tokens, replacing centralized, corporate platforms with open protocols and decentralized, community-run networks.
DAOs. A decentralized autonomous organization, or DAO, is an organizational structure built with blockchain technology that is often described as a crypto co-op. DAOs form for a common purpose, like investing in start-ups, managing a stablecoin or buying NFTs.
One of Mr. Belfort’s guests, Svein-Erik Nilsen, a Norwegian entrepreneur, started describing his own business ambitions. Did Mr. Hero have any tips? The key to starting a new venture, he replied, is aggressive marketing to stand out from the crowd. “Imagine going to a Brazilian beach and trying to find one single hot chick. There’s eight million,” Mr. Hero said. “The idea is the same thing here. You have to do stupid, dumb marketing to get it out there.”
A few hours later, the group adjourned for dinner at Carbone, a high-end Italian restaurant in Miami Beach where Mr. Belfort eats as often as twice a week. As they dined on caviar and rigatoni, some of the guests shared stories of their own debauchery; Mr. Belfort, it turned out, was not the only wolf in the room. Two guests discussed the mechanics of pursuing younger women without risking entanglement in a “sugar baby” situation. Someone speculated about how an enterprising strip club owner might incorporate NFTs into the business.
Soon conversation turned to a club in Japan where women are said to cavort with octopuses. Mr. Belfort wanted to know more: Were the women in Japan beautiful? Later, he showed the group an iPhone video he took at an S-and-M-themed bar, where the waitresses flog the customers.
Artem Bespaloff, the chief executive of the crypto mining company Asic Jungle, leaned across the table to describe his personal conversion to the way of the Wolf. He was planning to go to medical school, he said, when he found a copy of “The Wolf of Wall Street” at the library.
“I said, ‘This is what I want to do,’” Mr. Bespaloff recalled. “I ended up stealing the book from the library.”
“So I was a good influence,” Mr. Belfort said with a laugh. Still, he said, he regrets his behavior in those days — it was wrong, and he could have gotten even richer if he hadn’t broken the law. “I missed the internet boom,” he said. “I would’ve made 100x more money.”
“Well,” Mr. Bespaloff replied, “you’re in crypto now.”
“You live and learn,” Mr. Belfort said.
Audio produced by Adrienne Hurst.
Advertisement
Author
Administraroot